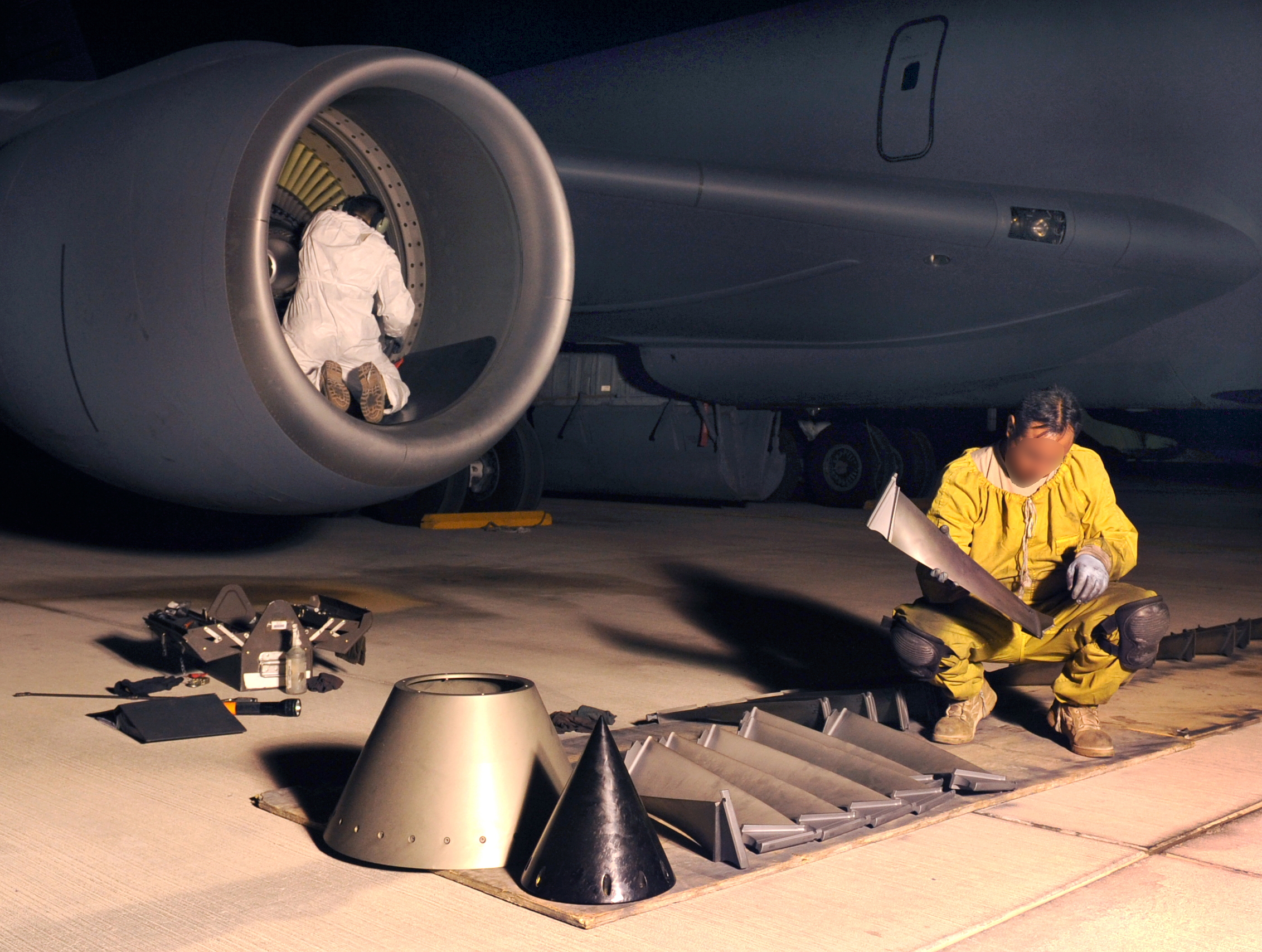
Non-destructive testing (NDT) is an examination of components or workpieces for their quality and structure that does not damage or impair them. It is regulated in the international standard DIN EN ISO 9712 and is used in various industrial sectors such as plant engineering, mechanical engineering, steel, power plant or vehicle construction.
NDT is subject to a strict certification process to prevent personal injury and damage to property. In this context, one also talks about finding and evaluating so-called discontinuities or imperfections, since the actual assessment of whether a defect is present is subject to the testing regulations.
Content
What types of non-destructive testing exist?
The 5 most important types of NDT are the following, they differ in the tools used and the evaluation e.g. imaging techniques.
- VT – Visual Testing
- MT – Magnetic Particle Testing
- PT – Penetrant Testing
- UT – Ultrasonic Testing
- RT/DR – Radiographic Testing and Digital Radioscopy
Other types are for example eddy current testing (ET), leak testing (LT), acoustic emission testing (AT) or thermographic testing (TT).
VT - Visual Testing
Visual Testing (VT) is an optical method to check objects for discrepancies. You can check with the naked eye as well as with tools like magnifying glasses or mirrors.
Many imperfections, such as external cracks, can already be found with visual testing, which makes this type of inspection a simple but powerful procedure. It can be used to check some imperfections of welds, fractured surfaces, corrosion phenomena or grinding.
MT - Magnetic Particle Testing
Magnetic particle testing (MT) is a method for testing magnetizable materials with a minimum of time. Magnetic particles are applied to the object to be tested with a liquid or powder. Inconsistencies are then revealed by a change in the magnetic field, which causes the particles to be aligned differently from the ‘good’ part of the object.
In this way cracks or inclusions of non-magnetic materials can be quickly detected. Especially remarkable is the detection of small cracks with a width of 0.001 mm and a depth of 0.01 mm. For comparison: a human hair has a thickness of 0.04 mm or more.
PT - Penetrant Testing
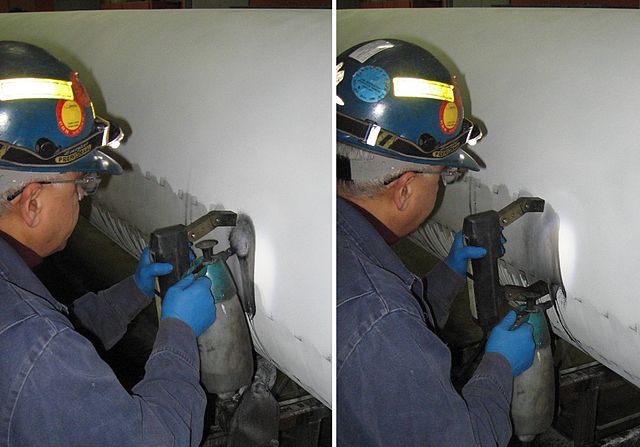
Penetrant testing (PT) is a flexible procedure that uses the capillary forces of cracks or pores. For this purpose, color or fluorescent penetrant (contraster) is applied to a cleaned component, e.g. with a spray can, followed by a ‘developer’. The penetrant then ‘creeps’ into the smallest cracks and reveals the imperfections. Important for the handling of the substances are environmental aspects, storage, disposal and correct transport. For dye penetrant testing, the colors red and white (contraster-developer) are usually used. Care should be taken with rough or brittle surfaces, as this can lead to so-called false readings, or with the color intensity, as these do not necessarily indicate the depth of a crack.
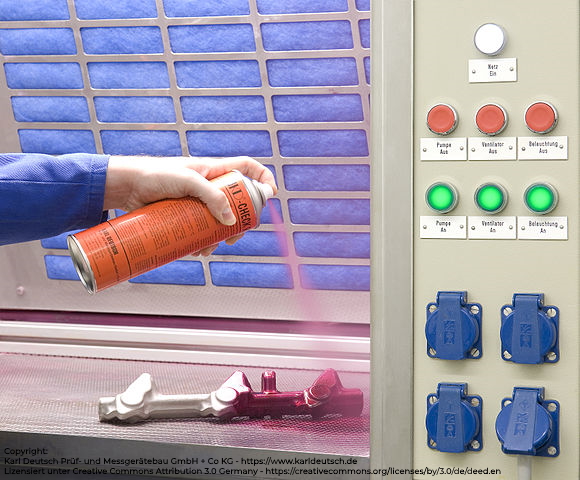 Penetrant Testing - application of the contraster
Penetrant Testing - application of the contraster
Karl Deutsch Prüf- und Messgerätebau GmbH + Co KG
https://www.karldeutsch.de
Licenced under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Germany
UT - Ultrasonic Testing
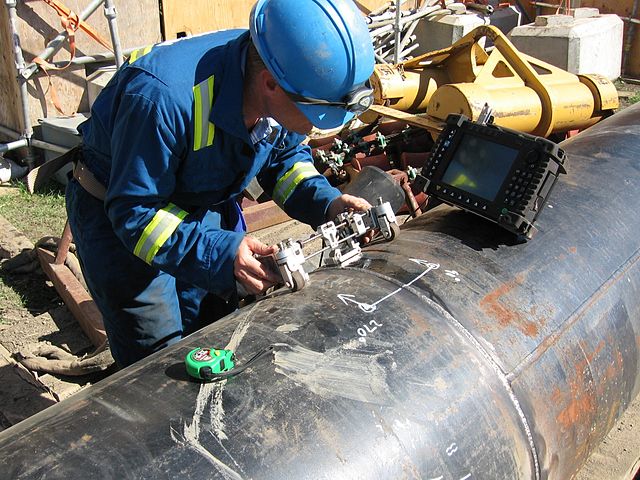
Ultrasonic testing (UT) allows a view into the inside of a component. To do this, a probe is moved over the surface of a component and the ultrasonic waves emitted by it or their reflections are tracked on a screen. A phased-array imaging test can also be performed, which allows easier interpretation. Both flat and voluminous imperfections can be inspected. In the case of surface imperfections, it is often superior to radiographic testing (RT). It is used, for example, for wall thickness measurement with vertical probes and for simple geometries with angle probes.
RT/DR - Radiographic Testing and Digital Radiography
Radiographic testing (RT) refers to an imaging test method that allows a view into the inside of a component. Depending on the component and size, an X-ray tube or radioactive material is used to irradiate a film. One advantage of this method compared to ultrasonic testing is that the type of imperfections, e.g. whether pore or slag, can be determined more easily. Since the handling of the preparations is subject to special safety regulations, the recording is often carried out by service providers. An evaluation of the imperfections can then be carried out separately. Digital Radiography (DR) using X-ray image intensifiers or radioscopy systems is becoming increasingly popular because images can be stored and evaluated digitally.

Which products/sectors are tested?
The most frequently tested components and products are:
- Castings – Pc
- Forgings – Pf
- Welded products – Pw
- Pipes and piping – Pt
- Rolled products – Pwp
A test can be carried out both during production and in the factory. Depending on the regulations and safety requirements for a component. The products and sectors are regulated in DIN EN ISO 9712 and also include some industrial sectors:
- Production – In
- Service inspection in production and maintenance – Is
- Railway maintenance – Ir
- Aerospace – Ia
and Thermographic Techniques:
- Active Thermography – TA
- Passive thermography – TP
- Active and passive thermography – TAP
Who may perform non-destructive testing?
Standard-compliant testing requires a certified inspector who, depending on experience and training, has achieved one of the following three levels in the respective test type (VT, MT, PT, UT, RT).
- Level 1: May perform test procedures and record the test results
- Level 2: May additionally evaluate test results according to standards and regulations
- Level 3: May additionally select test procedures, prepare procedure descriptions and is responsible for test facility
The test personnel must have good near vision and color vision. There are also rules of professional ethics which are intended to prevent personal injury and damage to property.
Various certification bodies such as TÜV NORD or the independent personnel certification body (DPZ) of the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT) or German Society for Non-Destructive Testing (DGZfP) issue certificates after a successful examination of the candidate. They themselves require confirmation from the German Accreditation Body (DAkkS) in order to be allowed to certify personnel in accordance with DIN EN ISO/IEC 17024:2012. The international standard DIN EN ISO 9712 requires that certificates must be renewed or recertified every 5 years.
How to reach a higher level?
What should you know about welds?
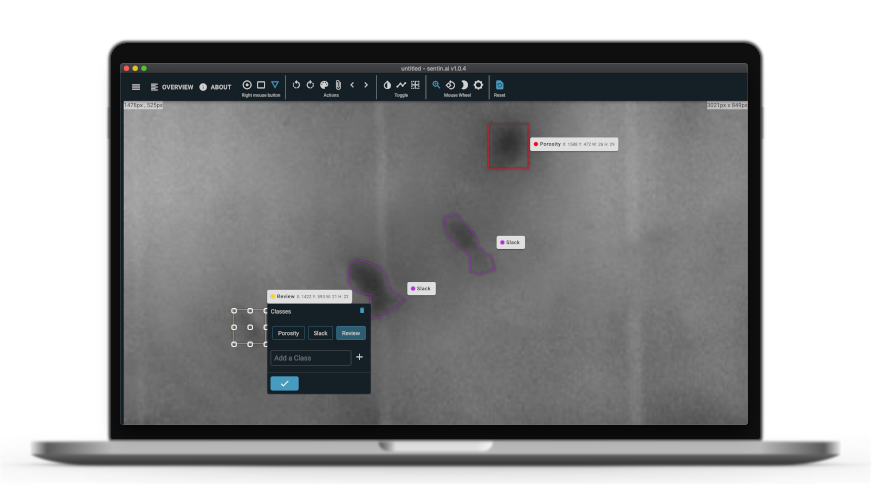
How can evaluation be performed digitally?
Digital radioscopy (DR) and working with imaging plates is becoming increasingly popular, but other imaging techniques such as Phased Array (UT) also offer image material that can be digitally evaluated. To save time and nerves during examination and evaluation, the right tool should be used. Often an interpretation of anomalies is also not clear, so one asks a colleague for advice. The sentin EXPLORER facilitates the evaluation by automatically analyzing and marking of imperfections.
Sources
- TÜV Nord – Non-destructive testing of materials and structures (NDT)
- American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT)
- DGZfP – Personell Certification
- GSI SLV Duisburg – Non Destructive Testing (German)
- Wikipedia – Different Testing Procedures