The industrial revolution is widely known. However, this article deals with the fourth revolution in non-destructive testing, the so-called NDT 4.0. It first discusses the development of industry and non-destructive testing and then some new technologies, as well as the advantages and use cases of NDT 4.0.
Inhalt
What is NDT 4.0?
The term “NDT 4.0” describes the fourth revolution in non-destructive testing. It relies on new technologies such as artificial intelligence, networked and decentralized systems (e.g. cloud) and other technical and digital solutions.
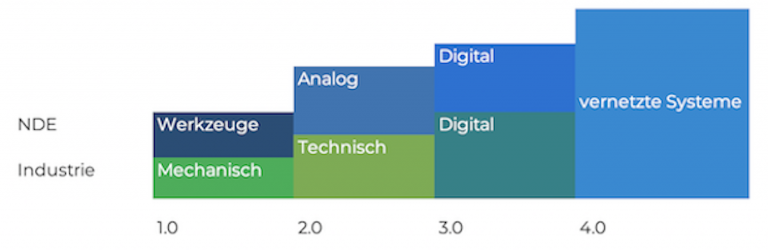
The NDT revolutions can be defined as follows:
- NDT 1.0 – Tools (to sharpen the senses)
- NDT 2.0 – Analog systems (for viewing within the components)
- NDT 3.0 – Digital processing and automation
- NDT 4.0 – Transparency of information, technical & digital aids and autonomous and decentralized decisions
It can be understood in a similar way to Industry 4.0. Its revolutions can be categorized as follows:
- Industry 1.0 – Mechanical (steam, energy)
- Industry 2.0 – Technical (electrical energy, mass production)
- Industry 3.0 – Digital (data processing, microelectronics)
- Industry 4.0 – Increasing digitalization, such as modern technologies and production as well as faster reactions to the sales market.
How do industry and NDT compare?
Industry and NDT are each divided into four revolutions. In the 1st and 2nd revolutions, there are still hardly any similarities. However, they are already very similar in the 3rd (digital stage). The NDT and NDE sectors and the industry are currently in the digital revolution. Both use networked systems that can make autonomous and decentralized decisions thanks to modern technologies and technical support.
What technologies does NDT 4.0 use?
NDT 4.0 is driven by many different technologies. It uses the following technologies, among others:
- Big Data & Artificial Intelligence
- Digital twins & simulations
- Cloud computing & storage
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- 5G
- Blockchain
- Augmented & virtual reality
Big data: Describes the increasing amounts of data that are available and analyzed with the help of modern systems. Companies that can use a longer history and a large amount of collected data are well prepared.
Artificial intelligence (AI): is a system that can interpret data and images, react to them and adapt. So-called neural networks are often used for this purpose. The subcategories of machine learning, which describes algorithms that improve with increasing data, and deep learning, which is based on neural networks and can improve with a lot of data even better, are particularly important for NDT 4.0.

Digital twins and simulations: On the basis of collected data, simulations can be used, for example, to make recommendations for action and predict decisions or events. The digital twin is then a digital entity that has exactly the same properties as the physical object. As a result, the behavior and condition of the real object can be precisely viewed and predicted. An AI can be used as the basis for such simulations.
Cloud Computing and Storage: Data can be securely stored in a cloud so that it can be accessed from any location. It consists of a distributed server network and offers redundant storage and a high level of compatibility thanks to modern web standards.
Internet of Things (IoT): All data, devices and sensors are connected with each other and can be accessed via a cloud. This can be a prerequisite for a good database and thus enable AI and digital twins. It is often abbreviated to IoT or IIoT for (Industrial) Internet of Things.
5G: Is a mobile data transmission technology and the successor to 4G/LTE and enables the connection of a large number of devices and ensures a robust real-time data connection. The large bandwidths enable the transmission of up to 10 Gbit/s, so that even large images or inspection results can be sent quickly.
Blockchain: With a secure blockchain, data can no longer be changed without being recognized, which improves traceability and trust. This can be interesting for archives, for example. Newer blockchain generations also make it possible to execute smart contracts, which are similar to smaller decentralized software programs.
Augmented / virtual reality: With the help of data glasses or intelligent displays, e.g. via the smartphone camera and display in real time, additional information and context-relevant representations can be shown to users. This can, for example, make it easier for inspectors to recognize the installation situation of components or certain work steps.
What advantages does NDT 4.0 offer?
The possibilities of NDT 4.0 create a number of advantages for user companies. The availability of lots of data, for example, makes it possible to use machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). With the help of such AI systems, for example, the inspection of systems and components can be improved, thereby increasing efficiency.
In addition, the efficiency of inspections can be increased through modern connectivity and advanced computers. Further more the tools may also increasingly simplify data exchange and feedback between customers and clients. Such systems are more reliable and inspections are easier to trace.
The benefits of NDT 4.0 can be categorized and summarized as follows:
- Improved NDT methods
- Improved equipment
- More control & traceability
- Simplified data transfer
- Better data evaluation
- Improvement of the production process
Advantage 1: Improved NDT merhods
Relevant technologies:
Cloud computing & storage – Decentralized evaluation
Artificial Intelligence – Critical Image Detection, Automatic Defect Recognition, Batch Processing
Robotics
Impact & examples:
NDT 4.0 utilizes a wide range of new technologies that improve current NDT methods. These have a direct impact on the way work is done in NDT.
For example, cloud computing enables decentralized evaluation of recordings and data. For example, data can be recorded at one facility and then transferred to an evaluation station at another location.
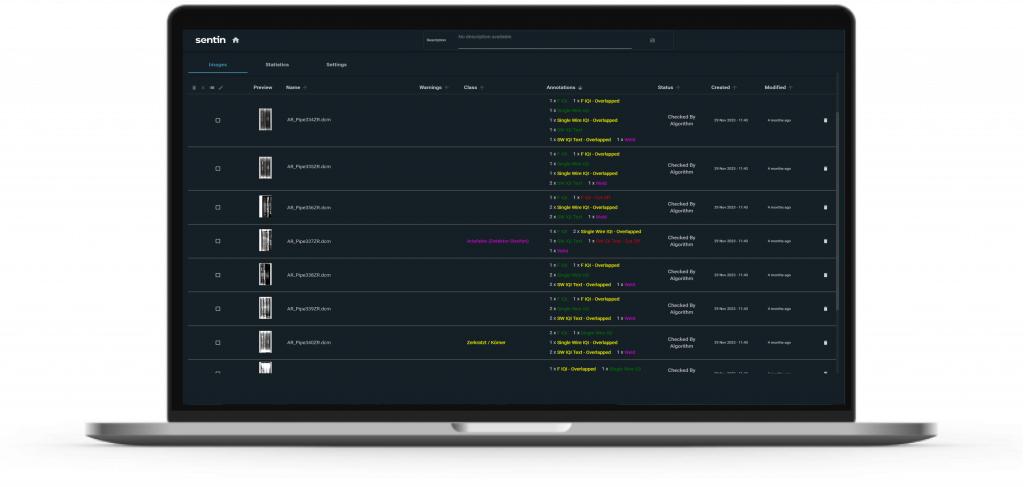
Another example could be the use of artificial intelligence (AI), for example to process all newly captured images of an X-ray inspection as a so-called batch. With the help of critical image detection, no time is wasted on “good images”, but the critical images that have poor quality or indications, for example, are found.
AI can also help to automatically detect indications and defects in inspection data and on images (ADR – Automatic Defect Recognition).
Other applications can include, for example, automatic recognition and assignment of texts, e.g. for a measuring point, or pattern recognition to detect suspicious or fraudulent activities (e.g. an image used several times for different measuring points).
You can find out more about decentralized evaluation and AI here.
Advantage 2: Improved Equipment
Relevant technologies:
Cloud computing & storage – digital archives, PACS, APIs
Artificial intelligence – super resolution, image enhancement
Robotics – crawlers, drones
New sensors & inspection technology
Augmented reality
Impact & examples:
The improvements to testing equipment as part of NDT 4.0 make it possible to test faster and more efficiently. Among other things, the improvements relate to the way in which humans and machines work together. The improved input and output of the devices can take the form of processed system and inspection information using augmented reality, automatic validation of results and meaningful error messages, for example.
Other methods can include data storage and processing, for example, so that the analog archive is replaced by a digital one. The so-called Picture Archiving & Communication Systems (PACS), ensure that the data is stored in an audit-proof manner. Together with interfaces such as DICOM/DICONDE or modern cloud APIs, the devices can be better connected.
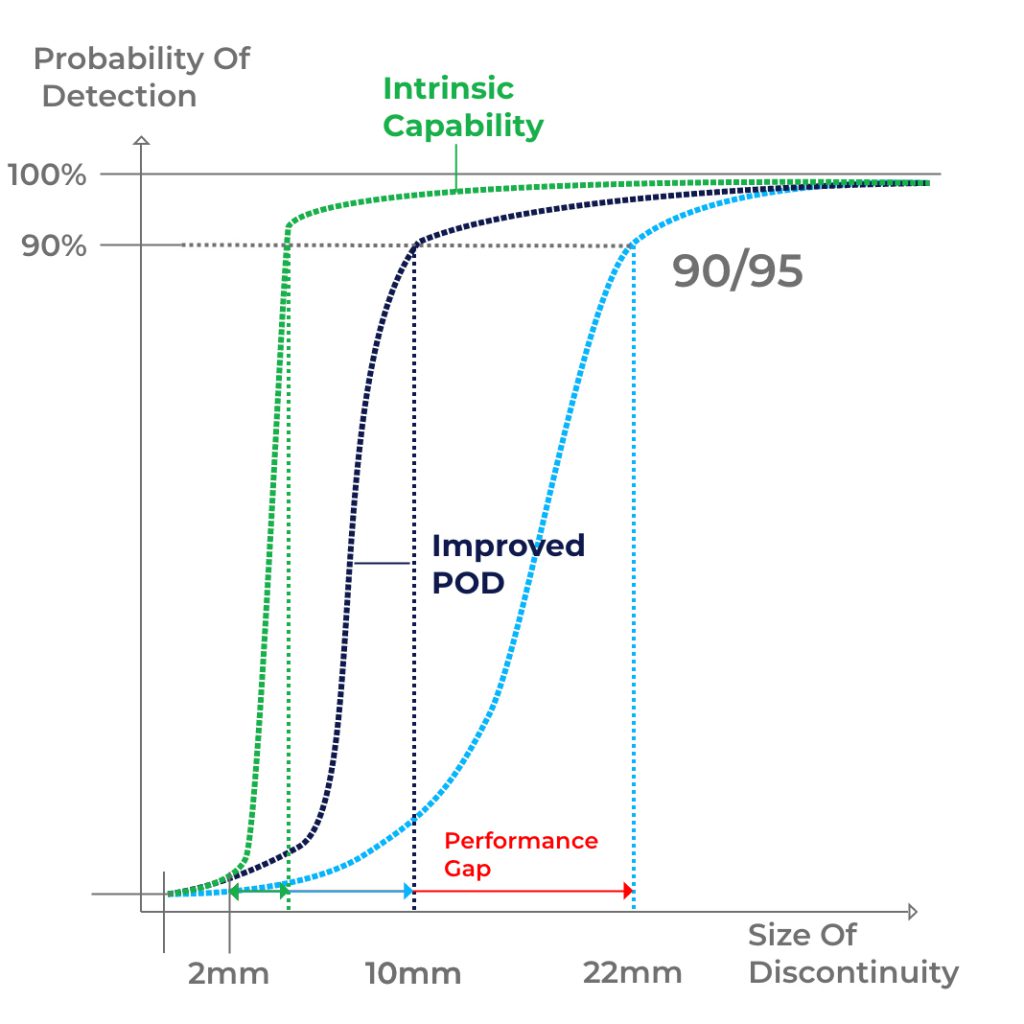
AI algorithms can also be used to achieve an improved representation of the recorded data. The “super-resolution” and “image enhancement” techniques are particularly interesting in this respect. For example, irradiation times can be reduced and more details can be found without having to accept greater image noise. A further consideration can be the improvement of the Probability Of Detection (POD), so that smaller and smaller defects can be found better.
Other applications include the use of intelligent robots, so-called “crawlers” and drones or new sensors and inspection technology. These networked devices make it possible to inspect systems or components automatically in some cases, e.g. in the thermography of solar systems or ultrasonic testing of large pipes. This has the simple advantage that even measuring points that are difficult to reach or large areas can be inspected with little effort and without the need for a person to climb up somewhere, for example.
Advantage 3: More control & traceability
Relevant technologies:
Cloud computing & storage – Digital archives, PACS
Digital interfaces – DICONDE
Digital twin
Data analytics
Impact & examples:
In NDT, there are various measures and standards that must be taken into account when conducting an inspection. One example is the traceability, which determines whether the check was carried out in the right place and with which procedures/parameters and according to which instructions. The implementation of audit-proof data storage is therefore necessary. The use of digital solutions from NDT 4.0, such as improved archives on the cloud and PACS solutions for storage or blockchains to protect against tampering, can help to increase this traceability. You can also store data in a more structured way and make it searchable more quickly.
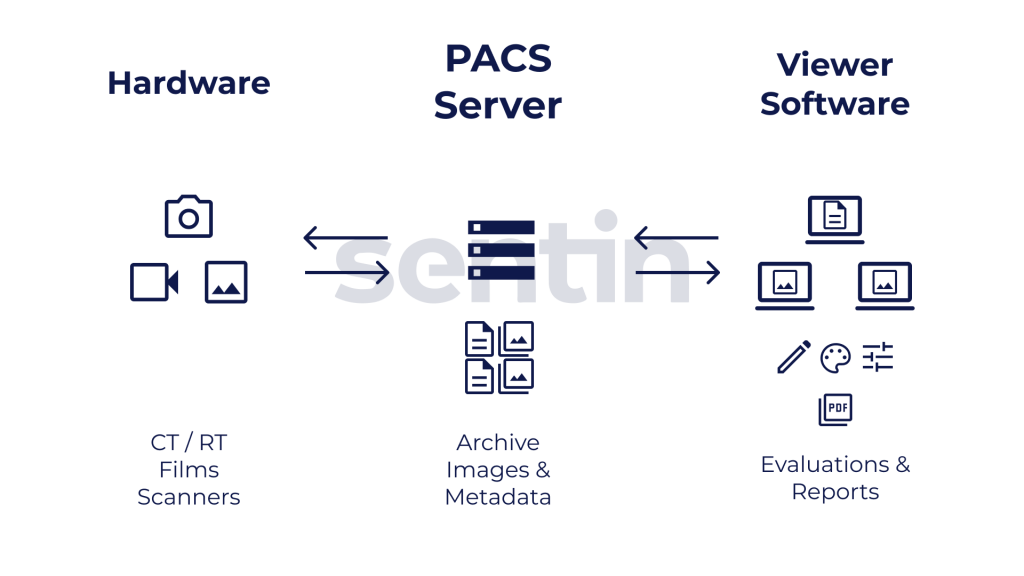
In addition, NDT 4.0 technologies and interfaces support the digital workflow by enabling the electronic transfer of inspection and order data. This enables paperless inspections and ensures greater overall control over processes and workflows. This is also necessary in order to derive new findings and recommendations for action with the help of data analytics and thus remain successful in the long term.
Advantage 4: Simplified data transfer
Relevant technologies:
Cloud computing & storage – Databases, APIs
Digital interfaces – DICONDE
5G
Impact & examples:
Networked systems and decentralized storage are important factors in NDT 4.0. Secure and fast transmission is necessary to make full use of these. Technologies such as 5G and modern interfaces make it possible to send data from the recording location to the evaluation station almost in real time and at the same time provide the manager with status information. User companies can benefit in particular from improved interoperability, allowing various solutions and devices to communicate with each other and thus enable more efficient testing.
Advantage 5: Better data evaluation
Relevant technologies:
Artificial intelligence
Data analytics
Big Data
Impact & examples:
NDT 4.0-supported understanding & transparency of data is a valuable competitive advantage. With structured data formats and a sufficient history, it is possible, for example, to make predictions for the future, create AI models and digital twins and optimize business processes. The challenge in NDT lies in the complexity of the inspection processes. With the help of data analytics, new insights can be gained and more efficient processes can be designed. For example, more precise service life calculations for components, predictive maintenance and reliability technologies are well known.
Advantage 6: Improvement of the production process
Relevant technologies:
Artificial intelligence
data analytics
Digital twin
New sensors & testing technology
Impact & examples:
NDT 4.0 also offers potential for improvement in production that goes beyond the traditional understanding of Industry 4.0 (such as predictive maintenance). One application, for example, could be faster and better quality assurance. If components can be inspected more quickly in production, for example, because an AI with super resolution is used for radiographic testing, this increases the efficiency of the production process from within NDT. In industry, NDT is often reduced to visual inspections with cameras or as a visual inspection by humans, but this falls short. In addition, digital archive systems in which the inspection data is stored provide an important basis for optimizing machine parameters in the production process, for example, based on the quality determined.
What are the challenges for NDT 4.0?
Despite all the benefits that NDT 4.0 brings, there are also some challenges. These challenges are primarily
- Technical hurdles, data and infrastructure
- Relevance of the skills learned
- Hesitant managers
- Insufficient understanding
Challenge 1: Technical hurdles, data and infrastructure
Although the new NDT 4.0 technologies mentioned above are developing rapidly, there are still some hurdles that are delaying their introduction into user companies. When it comes to artificial intelligence, for example, there are serious differences between consumer AIs, which are known for speech recognition and large language models such as ChatGPT or Google Bard, and industrial AIs, as the amount of data available in industry is much smaller. While millions of images of cats from the Internet can be used for consumer AIs, for example, the amount of public weld seam images for an industrial AI is close to zero. In addition, there is often no interest in making this data available to the competition.
Another factor can be supply bottlenecks or supply chains. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020/21, a lack of semiconductors and graphics cards became a problem for the industry. Since the energy crisis in Europe in 2022/23, the cost of maintaining the digital infrastructure has also increased.
Furthermore, there is of course a difference between research or the innovation departments of tech giants such as Google or Facebook and application in the field and in practice. It is well known that it takes some time for technologies tested in the laboratory to meet real-world requirements and for the necessary infrastructure to be established in the company.
Challenge 2: Relevance of the skills learned
The tasks and technologies of NDT 4.0 differ from traditional NDT functions and systems. Therefore, organizations that want to use these new technologies need to develop new skills. They need to acquire skills in information and communication technologies (ICT) and be able to work with intelligent systems such as collaborative industrial robots and desktops.
In addition, the people who will interact with these new advanced systems should have a flexible mindset. They should be prepared to accept that the knowledge they have today may become obsolete before the technology is used in the field.
NDT 4.0 requires employers and employees to learn more and faster than the previous revolution. Employers and their employees must see learning as an investment.
The skills required will also differ at different hierarchical levels. The evaluators in the field, for example, will need to receive training on new equipment. The managers will need to properly understand and manage the new digital processes, while corporate management will need to develop new business models. It will be crucial for them all to have the ability to learn and develop new skills faster than they were used to in previous innovations.
Challenge 3: Hesitant managers
Business leaders are often reluctant to introduce new innovations for a variety of reasons. One of these reasons is budgeting and the incentive for annual investment.
Companies seek short-term visible gains at the expense of greater and long-term intangible benefits. So, considering that NDT 4.0 is a long-term investment that requires higher technological investments and skills development, it may not be attractive for companies that are used to focusing on short-term gains.
Secondly, in most cases, people are extremely risk averse. They tend to focus on the uncertainties and problems, underestimating opportunities and potential. However, recent years have shown, both in industry and in NDT, that new technologies offer real added value and have arrived in practice. Companies that have invested early have been able to secure competitive advantages and overcome current challenges such as demographic change and the shortage of skilled workers.
NDT 4.0 therefore requires a new management style – Leadership 4.0, so to speak – flexible and digitally competent managers who know how to assess and use the new technologies with confidence.
Challenge 4: Insufficient understanding
NDT 4.0 offers many opportunities for inspection service providers, system operators and many other market participants. However, there is often little understanding of the technologies and a rather negative mentality. We occasionally hear that these technologies are not needed or that they are nothing special.
It is only when the potential of the technology is demonstrated and enriched with practical examples that it becomes clear how it can be used in your own company. At the latest with the large language models such as ChatGPT or Google Bard, artificial intelligence has at least reached the general public. For the NDT, the aim is to improve the understanding of auditors and managers through presentations, publications and training courses.
Furthermore, national associations such as the American, German or Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing (ASNT, DGZfP, ISNT) and their working groups offer various training and further education opportunities.
What do experts say about NDT 4.0?

Dr. Uwe Ewert
Expert for (Digital) Radiography
- Professor and Director off duty
- Chairman of the Technical Committee “Radiology” at the DGZfP for many years
- as well as former head of division at BAM and active at DGZfP
- Member of various standardisation committees of ISO, CEN and ASTM
- received the Berthold Award of the DGZfP (2005), the Röntgen Medal of the city of Remscheid (2009) and the Briggs Award of ASTM-International (2010).
How can I use NDT 4.0 today?
NDT 4.0 has already arrived in practice. Although it will certainly take some time before all companies are working entirely according to the principles, it is already possible to use some of the technologies presented.
Artificial Intelligence
Wall thickness measurements or corrosion – sentin GmbH
Weld seam defects – sentin GmbH
Text recognition / OCR – sentin GmbH
Duplicates, fraud and manipulation detection – sentin GmbH
Test data anonymization – sentin GmbH
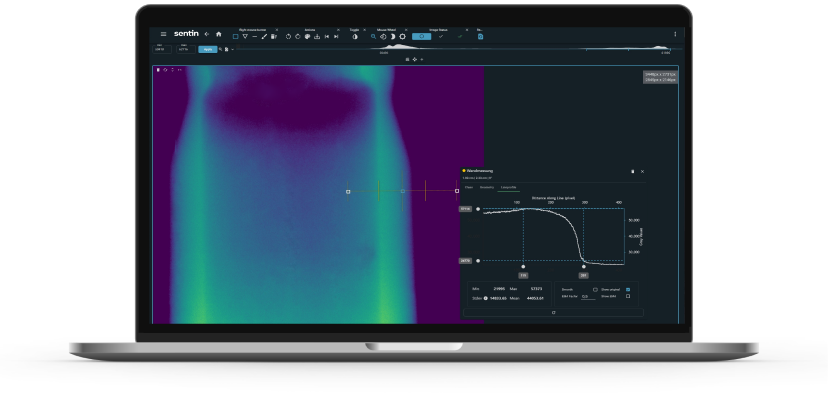
Automatic wall measurement of an entire pipe using AI.
Digital Tools and Workflows
Asset Collector - The app for photo documentation with automatic type plate recognition.

sentin EXPLORER - The imaging software with artificial intelligence and intelligent workflows.
Cloud & Infrastructure
Infrastructure & Integration Services – sentin GmbH
Automation solutions – sentin GmbH
Digital examination management – sentin GmbH
Examination archives and PACS – sentin GmbH & BW Plus NDT
Other
- Digital Archive – BW PLUS PACS
- NDT (Order) Management Software – DriveNDT
- Digital Twins – PipelineSentry
- Crawler / Robots – HausBots

Sources and further links
Literature:
- Dr. Johannes Vrana & Ripi Singh – “The NDE 4.0: Key Challenges, Use Cases, and Adaption”
- Maximilian Topp – “First Steps Towards NDT 4.0” – “ZfP heute Sonderbard 2020” – DGZfP – German Society Of Non-Destructive Testing
- Maximilian Topp – “How can NDT 4.0 improve the Probability of Detection (POD)?“ – “e-Journal of Nondestructive Testing (NDT)” ISSN 1435-4934 (NDT.net Journal)
- Christian Els – “KI in der zerstörungsfreien Prüfung – Wie die Digitalisierung zu einer automatisierten Zukunft in der ZfP führt” – DGZfP-Berichtsband BB 180 | ISBN 978-3-947971-29-9 | DGZfP
- Christian Els – “How AI will shape the future of NDT – the practical example of AI-based
X-Ray Weld Interpretation.” 13th International Symposium on NDT in
Aerospace, 2021







