Non-destructive testing (NDT) has been an integral part of modern science and technology. It has provided an array of techniques to detect and analyze defects in components, materials and systems or without causing further damages. The testing method, which boasts a market size value of USD 14.6 billion, has gone through a great deal of evolution over the centuries. Therefore, the history of NDT is long and can occupy thousands of pages if it was to be written down entirely. To give a quick glance into the history, this article handpicks the five most interesting facts of the history.
If you want to learn more about non-destructive testing, be sure to check out our other articles:
Facts
People begin to recognize NDT as a technology
1920s and before
By the time the expression NDT was invented in 1920s, the ancient people had already been using techniques that followed the principles of nondestructive testing for centuries. For instance, they could analyze objects with their naked eyes to identify the presence of visible surface flaws without causing damages to the objects. Blacksmiths used to listen to different metals when shaping metal to ensure that they applied the right force to the right metal to produce the desired shapes.
World War II - Catalyst for NDT evolution
1930s and 1940s
The global war, that occurred between 1939 to 1945 led to the invention of the NDT technologies and devices that are still applicable in modern day science and technology.
For instance, the aircrafts that were used during the war were made of light non-magnetic metals, necessitating a different testing approach to replace magnetic testing. The need resulted in penetrant testing using fluorescents and dye penetrants.
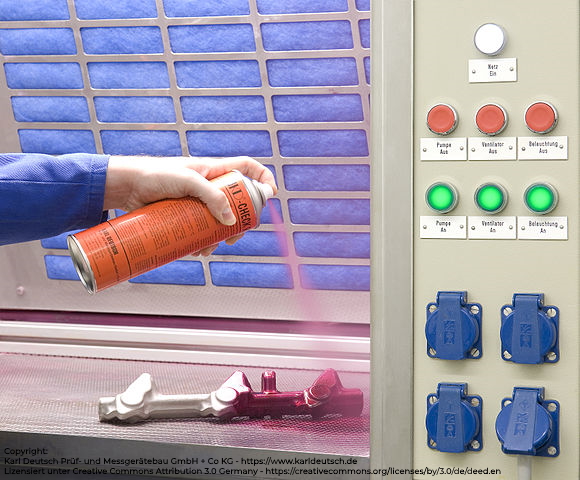 Penetrant Testing - application of the contraster
Penetrant Testing - application of the contraster
Karl Deutsch Prüf- und Messgerätebau GmbH + Co KG
https://www.karldeutsch.de
Licenced under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Germany
Radiographic Testing
1940s and after
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, the inventor of the x-ray technique, discovered “An Unknown Kind of Radiation” that could help in flaw detection. This discovery led to the development of an x-ray equipment that was majorly used in the medical field. However, ray had not foreseen the possible grave adverse effect that X-rays would have on human health. As a result, a lot of people who got exposed to the electromagnetic waves died.
To curb the deaths and other related health complications radiation protection clothing has been invented. Later, the U.S. X-ray and Radium Protection Advisory Committee introduced the first formal standard aimed at protecting humans from X-ray sources.
In the 1930s and 1940s early radiographic testing took place. Until today it is a common solution to find defects inside of materials and products.
Read more about it here:
“5 Benefits of Digital Radioscopy (DR)”
Foundation of Eddy Current Testing - Hans Christian and Michael Faraday
1948 to 2012
Although Leon Foucault, a French physicist, discovered the phenomenon of eddy currents in 1851, this discovery was inspired by the discovery of electromagnetic induction by Michael Faraday, an English scientist in 1831, and electromagnetism discovery by Hans Christian in 1820.
During World War II the NDT method relying on Eddy Current has been further developed. In 1948 Friedrich Foerster in Germany founded a company to develope equipment based on this method.
Until today the market for Eddy Current Testing is growing and was estimated to have a size of 220$ million in 2012.
Eddy current testing is an NDT technique that uses principles of electromagnetic induction to detect surface and sub-surface flaws.

NDT applications keep on increasing
2010s and after
The global automation and robotics sector is growing 24/7, creating more demand for reciprocating processors to speed up workflows and cut down on labour costs. For instance, NDT sensors are integrated with industrial robots and cobots for damage-free automated inspection systems that are popularly used in production inspection as well as research and development. With a recent Robotics Business Review report showing that a total investment of US$1.16 billion were injected into the robotics sector in 2020, it’ll be reasonable to expect NDT applications to become even more popular and helpful going forward.
Non-destructive testing techniques have evolved for hundreds of years, and they are still getting better in terms of efficiency, safety and accuracy with time. The above five are among the interesting facts that you need to need to know about the history of NDT.
NDT 4.0 - Combines new technologies
2020s and after
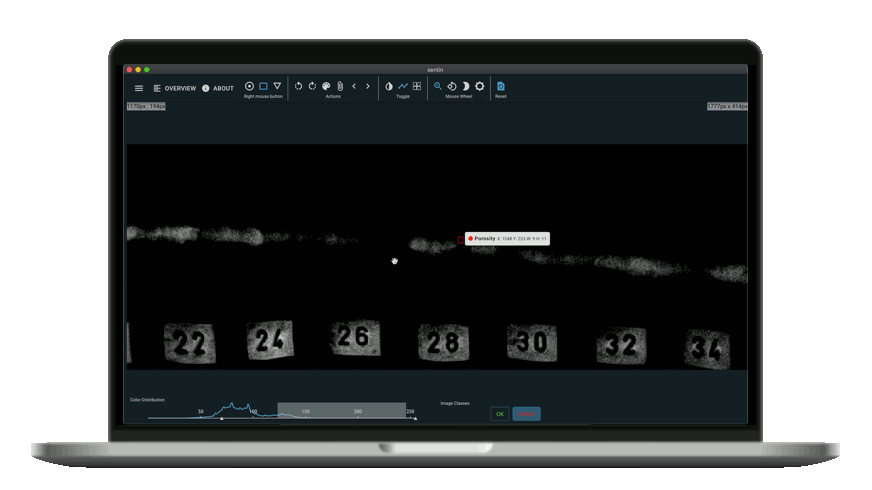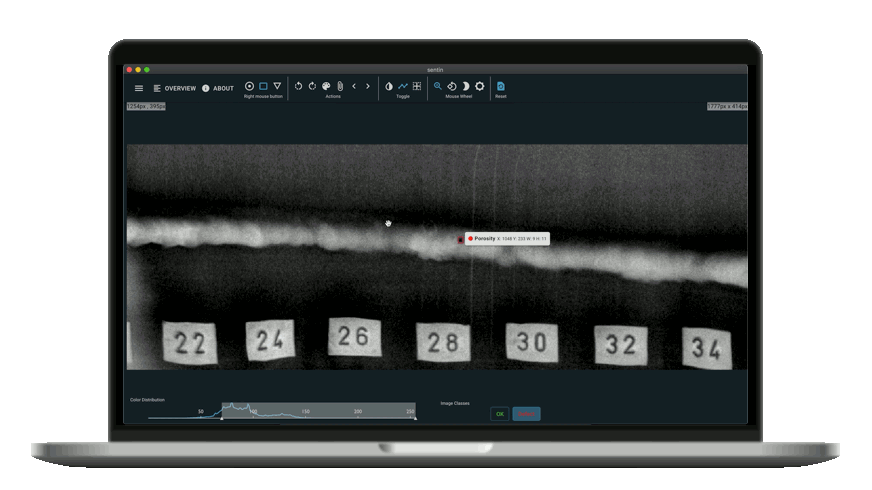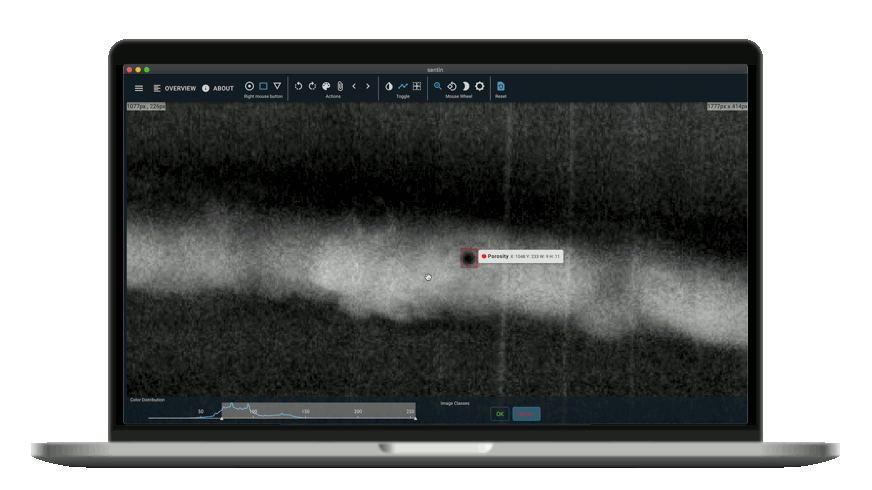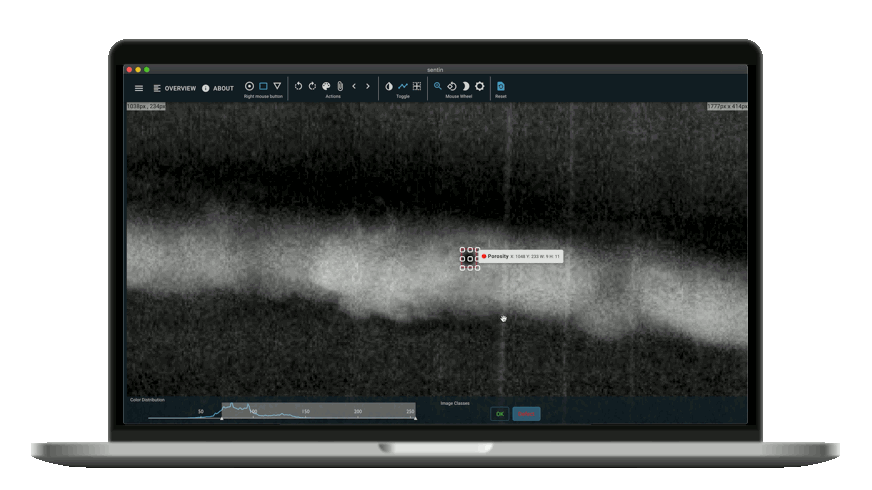
Nowadays, NDT has developed strongly. It also could not avoid digitalization and software development. One of the most interesting points of contact is with Artificial Intelligence. An example is image analysis software that supports the inspectors or even automates the processes completely. One such software is the sentin EXPLORER.
This new field of NDT is called NDT 4.0 and uses several modern technologies to boost non-destructive testing. You can read more about it here:

The sentin EXPLORER is a tool to automate such inspection or image evaluation tasks. Our customers sometimes produce thousands of images per week, all of which have to be reliably checked. Therefore we give you the power to perform evaluations with the help of artificial intelligence and to find defects more reliably or gain new insights.